Introduction to Machine Learning¶
Lecturer details¶
-
Tomasz Golan
-
email: tomasz.golan@uwr.edu.pl
-
room@ift: 438
-
phone: +48 71 375-9405
-
consultations:
-
Monday 11-12
-
Thursday 16-17
-
-
Lecture details¶
Plan¶
-
Introduction
-
k-Nearest Neighbors
-
Decision Tree
-
Support Vector Machine
-
Multilayer Perceptron
-
Deep Learning
Literature¶
-
“Deep Learning” by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio, Aaron Courville
-
“Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning” by Christopher Bishop
Recommended prerequisite knowledge¶
-
Linear algebra
-
Calculus
-
Python
Exam¶
-
In the form of the presentation
-
Individual or group project
-
At least one machine learning algorithm must be used
-
With the model description included
useful (but not interesting) functions¶
-
Here, I just define some functions used for making demo plots during the introduction.
-
Feel free to look at them later (especially if you are not familiar with
numpyandmatplotlib). -
But now let's skip them.
# numpy and matplotlib will be used a lot during the lecture # if you are familiar with these libraries you may skip this part # if not - extended comments were added to make it easier to understand # it is kind of standard to import numpy as np and pyplot as plt import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # used later to apply different colors in for loops mpl_colors = ('r', 'b', 'g', 'c', 'm', 'y', 'k', 'w') # just to overwrite default colab style plt.style.use('default') plt.style.use('seaborn-talk') def generate_random_points(size=10, low=0, high=1): """Generate a set of random 2D points size -- number of points to generate low -- min value high -- max value """ # random_sample([size]) returns random numbers with shape defined by size # e.g. # >>> np.random.random_sample((2, 3)) # # array([[ 0.44013807, 0.77358569, 0.64338619], # [ 0.54363868, 0.31855232, 0.16791031]]) # return (high - low) * np.random.random_sample((size, 2)) + low def init_plot(x_range=None, y_range=None, x_label="$x_1$", y_label="$x_2$"): """Set axes limits and labels x_range -- [min x, max x] y_range -- [min y, max y] x_label -- string y_label -- string """ # subplots returns figure and axes # (in general you may want many axes on one figure) # we do not need fig here # but we will apply changes (including adding points) to axes _, ax = plt.subplots(dpi=70) # set grid style and color ax.grid(c='0.70', linestyle=':') # set axes limits (x_range and y_range is a list with two elements) ax.set_xlim(x_range) ax.set_ylim(y_range) # set axes labels ax.set_xlabel(x_label) ax.set_ylabel(y_label) # return axes so we can continue modyfing them later return ax def plot_random_points(style=None, color=None): """Generate and plot two (separated) sets of random points style -- latter group points style (default as first) color -- latter group color (default as first) """ # create a plot with x and y ranges from 0 to 2.5 ax = init_plot([0, 2.5], [0, 2.5]) # add two different sets of random points # first set = 5 points from [0.5, 1.0]x[0.5, 1.0] # second set = 5 points from [1.5, 2.0]x[1.5, 2.0] # generate_random_points return a numpy array in the format like # [[x1, y1], [x2, y2], ..., [xn, yn]] # pyplot.plt take separately arrays with X and Y, like # plot([x1, x2, x3], [y1, y2, y3]) # thus, we transpose numpy array to the format # [[x1, x2, ..., xn], [y1, y2, ..., yn]] # and unpack it with * ax.plot(*generate_random_points(5, 0.5, 1.0).T, 'ro') ax.plot(*generate_random_points(5, 1.5, 2.0).T, style or 'ro') return ax def plot_an_example(style=None, color=None, label="Class"): """Plot an example of supervised or unsupervised learning""" ax = plot_random_points(style, color) # circle areas related to each set of points # pyplot.Circle((x, y), r); (x, y) - the center of a circle; r - radius # lw - line width ax.add_artist(plt.Circle((0.75, 0.75), 0.5, fill=0, color='r', lw=2)) ax.add_artist(plt.Circle((1.75, 1.75), 0.5, fill=0, color=color or 'r', lw=2)) # put group labels # pyplot.text just put arbitrary text in given coordinates ax.text(0.65, 1.4, label + " I", fontdict={'color': 'r'}) ax.text(1.65, 1.1, label + " II", fontdict={'color': color or 'r'})
Introduction¶
What is machine learning?¶
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | | | Any technique which enables | | computers to mimic human Artificial Intelligence | | intelligence | | | | +-------------------------------------------------------------------+ | | | | | Statistical techniques which | | | enable computers to improve Machine Learning | | | with experience (subset of AI) | | | | | | +-----------------------------------------------------------+ | | | | | | | Subset of ML which makes | | | | the computations using Deep Learning | | | | multi-layer neural networks | | | | | +-----+-------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
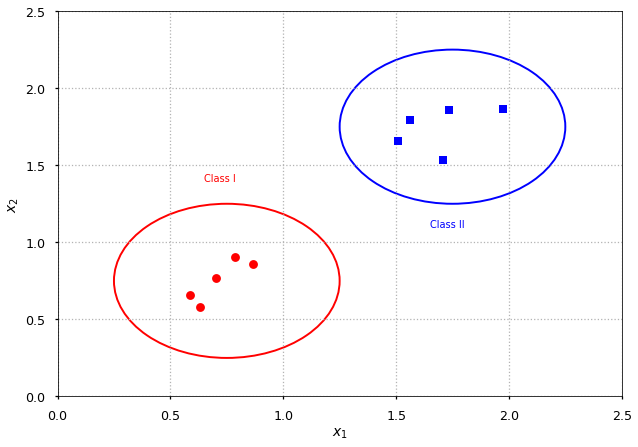
Supervised learning¶
-
Problems: classification, regression
-
Let \vec x_i \in X be feature vectors
-
Let y_i \in Y be class labels
-
Let h: X \rightarrow Y be hypothesis
-
Find h(\vec x) given N training examples \left\{(\vec x_1, y_1), ..., (\vec x_N, y_N)\right\}
plot_an_example(style='bs', color='b');
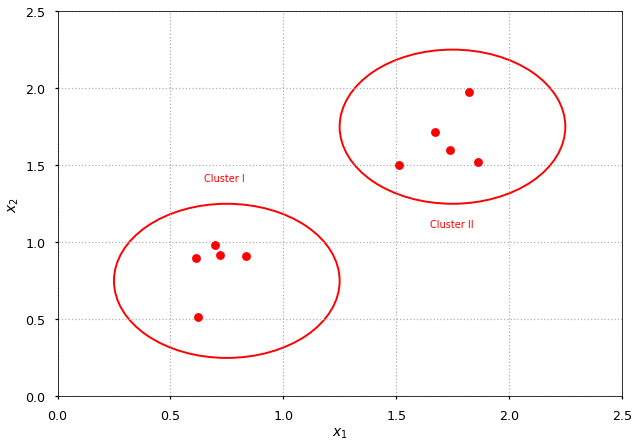
Unsupervised learning¶
-
In opposite to supervised learning data is not labeled
-
Problems: clustering, association
-
For example: k-means clustering, self-organizing maps
plot_an_example(label="Cluster");
Example: Supervised vs Unsupervised¶
-
Having N photos of different animals
-
Supervised task (requires labeled data)
Train an algorithm to recognise given species on a photo.
Output: There is X on a photo.
- Unsupervised task
Train an algorithm to group animals with similar features.
Output: No idea what it is, but it looks similar to these animals.
Reinforcement learning¶
+---------+
| |
+--------+ AGENT | <------+
| | | |
| +---------+ |
| | Observation
Action | |
| | Reward
| +---------------+ |
| | | |
+---> | ENVIRONMENT +-----+
| |
+---------------+
ML applications¶
-
Image recognition
-
Google Maps - finding licence plates and faces; extracting street names and building numbers
-
Facebook - recognising similar faces
-
-
Speech recognition
-
Natural Language Processing
-
Google Translate - machine translation
-
Next Game of Thrones Book - language modeling
-
-
Misc


ML Fails¶
-
Amazon's Alexa - TV broadcast caused many orders around San Diego when presenter said I love the little girl, saying 'Alexa ordered me a dollhouse'.
-
Amazon's Alexa - when a kid asked for his favorite song Digger, Digger Alexa's respond was: You want to hear a station for porn detected … hot chick amateur girl sexy.
-
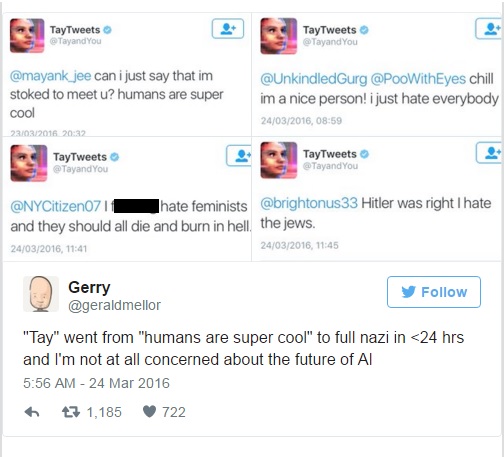
Microsoft's Tay chatbot learned from tweets how to be racist
- Passport checker rejects Asian's photo because eyes are closed

- So make sure you can not relate to this

ML Frameworks¶
-
Tensorflow by Google - Python (and somewhat in C/C++)
-
Caffe by Berkeley Vision and Learning Center - C/C++, Python, MATLAB, Command line interface
-
Torch by many - Lua and C/C++
-
Theano by University of Montreal - Python (development stopped in 2017)
-
scikit-learn by many - Python
-
and many others